The Role of Serological Markers in Dengue Diagnosis
Dengue has become an infection of great concern in India and a serious health problem worldwide. Dengue fever is an acute infectious disease caused by four serotypes of Dengue Virus (DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3 & DENV-4), and is the most prevalent mosquito-borne viral disease in humans, occurring in about 128 countries, where over 3.9 billion people are at risk of infection.
Dengue has a wide spectrum of clinical symptoms, often with unpredictable evolution and outcome. While most patients recover following a self-limiting non-severe clinical course, a small proportion progress to severe disease, Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever or Dengue Shock Syndrome, characterized by plasma leakage with or without hemorrhage. Early recognition is challenging because the initial symptoms are often non-specific, viremia may be below detectable levels and diagnostic tests may confirm Dengue later in the course of disease.
Prompt diagnosis during the febrile stage is essential for adjusting appropriate management of the disease.
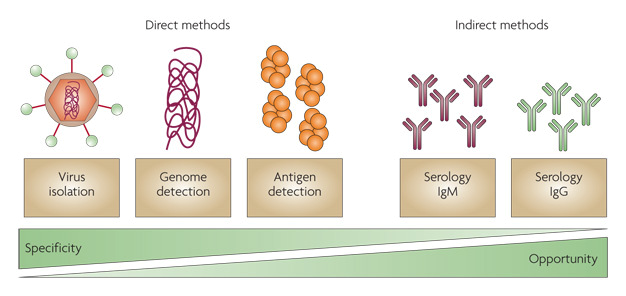
Image 1 - Direct and indirect diagnostic methods for Dengue
Direct diagnostic methods such as dengue virus isolation, genome detection, and antigen detection are more specific ways to diagnose dengue than indirect methods that detect IgM and IgG antibodies against dengue. There is a greater opportunity for diagnosis with the indirect tests because these diagnostic methods are typically the most practical options available.
© 2010 Nature Publishing Group Peeling, R. W. et al. Evaluation of diagnostic tests: dengue. Nature Reviews Microbiology 8, S30–S37 (2010). All rights reserved.
Serological diagnosis of Dengue infection is primarily based on the detection of three main markers, namely – Dengue NS1 Antigen and IgM/IgG Antibody against Dengue virus.
Dengue NS1 Antigen:
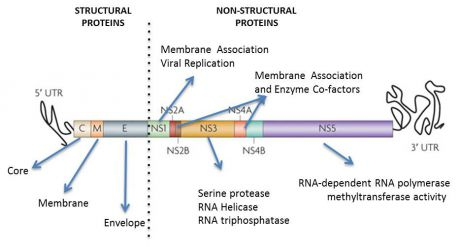 Image 2 - Dengue Virus Genome
Image 2 - Dengue Virus Genome
Dengue NS1 antigen (Non-Structural Protein 1) is a highly conserved glycoprotein common to all the four serotypes of Dengue Virus and therefore, an important early marker of the infection. Though it does not seem to have any biological and precise function, yet it is essential for virus viability or replication, and is released in a soluble form, from the infected mammalian cells.
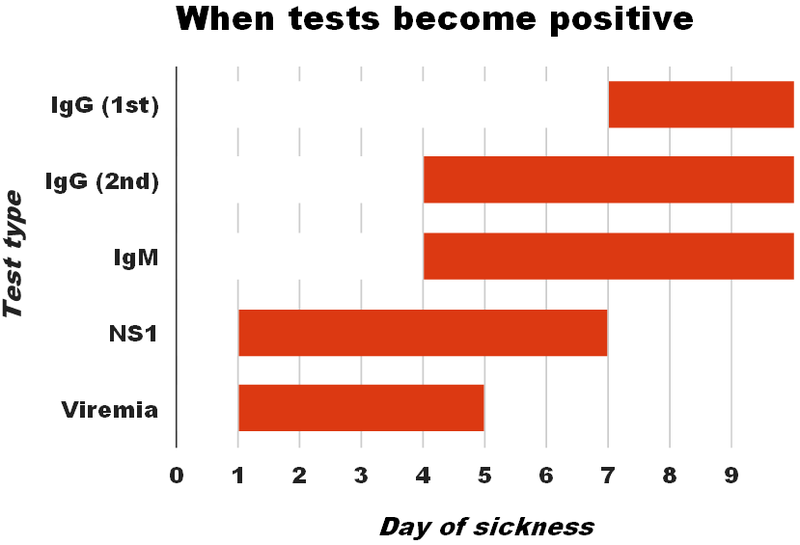
NS1 antigen is found circulating in high concentrations in human serum during the acute phase of the disease and so can be detected in patient’s serum/plasma, 1-9 days after the onset of fever. Detection of Dengue NS1 antigen by ELISA allows early diagnosis of infection, even prior to seroconversion which subsequently allows earlier monitoring, possibly reducing the risk for DHF/DSS.
IgM Antibody against Dengue Virus
IgM class of antibodies is the first to be produced in a usual course of Dengue infection. However, the time to IgM production varies considerably among patients. Some patients have detectable IgM by the 3rd day of symptoms; others do not develop detectable IgM until the 8th day of symptoms. Levels in the blood rise for a few weeks, then gradually decrease. After a few months, IgM antibodies fall below detectable levels.
IgG Antibody against Dengue Virus
IgG antibodies are produced more slowly in response to an infection. Typically, the level rises with an acute infection, it stabilizes, and then persists long-term. Individuals who have been exposed to the virus prior to the current infection maintain a level of IgG antibodies in the blood that can affect the interpretation of diagnostic results.
| IgM Result |
IgG Result |
Possible Interpretation |
| Positive |
Negative |
Current Infection |
| Positive |
Positive |
Current Infection |
| Low or negative or not tested |
Four-fold increase in samples taken 2-4weeks apart |
Recent Infection |
| Low or negative |
Positive |
Past Infection |
| Negative |
Negative |
Too soon after inital exposure for antibodies to develop or symptoms due to another cause |
Positive IgM and IgG tests for dengue antibodies detected in an initial blood sample mean that it is likely that the patient got infected with the dengue virus in the past few weeks.
If the IgG is positive but the IgM is low or negative, then it is likely that the patient had an infection sometime in the past.
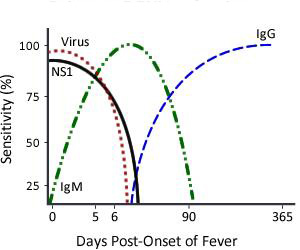 Image 4 - Primary Dengue Infection
Image 4 - Primary Dengue Infection
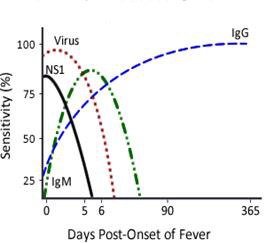 Image 5 - Secondary Dengue Infection
Image 5 - Secondary Dengue Infection
A primary dengue infection is characterized by a slow and low titer antibody response. IgM antibody is the first immunoglobulin isotype to appear. These antibodies are detectable in 50% of patients by days 3-5 after onset of illness, increasing to 80% by day 5 and 99% by day 10. Anti-dengue IgG is detectable at low titer at the end of the first week of illness, and slowly increases.
During a secondary dengue infection, antibody titers rise rapidly. The dominant immunoglobulin isotype is IgG, which is detectable at high levels, even in the acute phase. At early stages, IgM levels are significantly lower in secondary infections than in primary ones and may be undetectable in some cases.
Patients with severe Dengue illnesses can be treated efficiently if they are diagnosed as early as possible. The ideal diagnostic test for Dengue would be highly sensitive during the acute stage of the infection, able to distinguish Dengue from other diseases with similar symptoms, quick and easy to use, and affordable.
Dengue NS1 antigen ELISA is a very useful and specific tool in diagnosing cases of acute Dengue infection as it has a distinct advantage of being able to detect Dengue antigen from the 1st day of the symptoms. When combined with IgM antibody ELISA, it can significantly improve diagnostic efficacy in Dengue infection. This can definitely help resource–limited countries like India which experiences outbreak annually and it is a seasonal trend.
Serological diagnosis of Dengue infection via detection of IgM and IgG by Immuno-capture ELISA has distinct advantages over the Indirect ELISA format: ease of performance in testing, sensitivity in detecting acute phase antibodies and non-requirement of sophisticated equipment.
ErbaLisa Dengue ELISA kits.
In addition to our instruments, Erba LisaScan EM – Automated microplate ELISA reader and Erba Lisa Wash II - Automated microplate ELISA washer; Transasia Bio-medicals now offers comprehensive range of ELISAs, which provide a Reliable, Accurate and Affordable solution for the diagnosis of Dengue.
ErbaQik Dengue Rapid Tests
ErbaQik Rapid Tests for Dengue introduces a unique concept of ‘Dual Color detection system’. The results are clear and easy to interpret due to distinct red control and black test bands. We are the pioneers in using a differently sized gold nanoparticle conjugate, termed as ‘Black Gold Particle’. This helps us achieve much superior sensitivity and specificity than the competitors. Also, use of this black gold particle minimizes the chances of appearance of the ‘Ghost Bands’ due to reverse flow of the sample in the test window.
With proven superior sensitivity and specificity and simple protocol, Transasia Bio-medicals offers a complete solution for all kinds of laboratory set-ups. ErbaLisa Dengue ELISAs and ErbaQik Dengue Rapid tests are designed to be user-friendly and require minimal infrastructure and training, ensuring early, sensitive and reliable diagnosis of Dengue infection.
References:
- Detection of Dengue infection by combining the use of an NS1 antigen based assay with antibody detection. Anita Chakravarti, Amod Kumar and Sonia Malik, Dept. of Microbiology, Maulana Azad Medical College and Associated Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health, vol 42, no.2, March 2011.
- High Circulating levels of the Dengue Virus Nonstructural 1 Protein NS1 early in Dengue illness correlate with the development of Dengue. Daniel H. Librarty et al. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2002; 1861165-8.
- Virological and Serological Markers in Dengue Patients from Venezuela and Nicaragua. Ruiz, D., Vázquez, S., Villegas, E., Balmaseda, A., Pupo, M., Alvarez, M., Rosario, D., Bendezu, H., Calzada, N. and Guzman, M.G. (2017)
- Virological and Serological Markers in Dengue Patients from Venezuela and Nicaragua. Open Access Library Journal, 4: e3309.
- Association of platelet count and serological markers of dengue infection- importance of NS1 antigen. RD Kulkarni, SS Patil, GS Ajantha, AK Upadhya, AS Kalabhavi, RM Shubhada, PC Shetty, PA Jain. Indian Journal Of Medical Microbiology 2011; vol 29; Issue 4; 359-362.
- Dengue NS1 antigen detection: A useful tool in early diagnosis of dengue virus infection. S Datta, *C Wattal. Department of Clinical Microbiology, Sir Ganga Ram Hospital. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology, Vol. 28, No. 2, April-June, 2010, pp. 107-110.
- Diagnosis of Dengue Virus Infection by Detection of Specific Immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgA Antibodies in Serum and Saliva. Angel Balmaseda et al. Clin Vaccine Immunol March 2003 vol. 10 no. 2 317-322.
- Evaluation of NS1 antigen capture ELISA and IgM antibody capture ELISA in acute cases of Dengue in rural population in a tertiary care teaching hospital in western Uttar Pradesh, India. Rajesh Kumar Verma et al. Department of Microbiology, UPRIMS&R, Saifai, Etawah (UP), India.IJPSR.0975-8232.7(4).1780-84.