Hepatitis B and C are significant global health concerns, affecting hundreds of millions of people worldwide. In India, as per the latest estimates, 40 million people are chronically infected with hepatitis B and six to 12 million people are chronically infected with hepatitis C.1 Early detection and diagnosis of these viral infections are crucial for effective treatment, preventing the spread of the disease, and reducing long-term health complications. From a diagnostics perspective, timely and accurate detection methods such as rapid tests and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) play a pivotal role in managing these diseases.
Importance of Early Detection
Hepatitis B and C viruses (HBV and HCV) primarily affect the liver, leading to conditions ranging from acute hepatitis to chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Often, these infections are asymptomatic in the early stages, making early detection challenging yet critical. Timely diagnosis allows for prompt intervention, reducing the risk of transmission and improving the prognosis for affected individuals.
Diagnostic Methods for Hepatitis B and C
Several diagnostic tests are available for detecting HBV and HCV infections. These tests vary in complexity, accuracy, and speed. Among the most commonly used methods are rapid tests and ELISA, both of which have distinct roles in the diagnostic process.
Rapid Tests
Rapid tests are point-of-care diagnostics designed to provide quick results, usually within 15-30 minutes. These tests are particularly valuable in settings where access to laboratory facilities is limited or when immediate results are necessary.
Advantages of Rapid Tests:
-
Speed: Rapid tests deliver results in a short time, facilitating immediate clinical decisions.
-
Convenience: These tests are easy to administer, requiring minimal training and no specialized equipment.
-
Accessibility: Ideal for use in remote or resource-limited settings, increasing the reach of diagnostic services.
Rapid tests typically detect antigen and antibodies to HBV and HCV respectively, indicating exposure to the viruses. For example, the HBsAg rapid test detects the presence of the hepatitis B surface antigen, a marker of active HBV infection. Similarly, HCV rapid tests detect antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, suggesting an ongoing or past infection.
ELISA Tests
ELISA is a laboratory-based technique that is widely regarded as the gold standard for the detection of hepatitis infections. It involves the binding of viral antigens to specific antibodies, followed by a series of reactions that produce a measurable signal, usually a color change, indicating the presence of the virus.
Advantages of ELISA Tests:
-
High Sensitivity and Specificity: ELISA tests are highly accurate, reducing the likelihood of false positives and negatives.
-
Quantitative Results: These tests can provide quantitative data, such as viral load, which is essential for monitoring disease progression and response to treatment.
-
Reliability: ELISA is a well-established method with consistent and reproducible results.
For hepatitis B, ELISA tests can detect various markers, including HBsAg, anti-HBs, and anti-HBc, providing a comprehensive profile of the infection status. In the case of hepatitis C, ELISA tests primarily detect anti-HCV antibodies.
Rapid and ELISA tests play a crucial role in the timely detection of hepatitis B and C. Rapid tests provide quick results, often within 20 to 30 minutes, making them ideal for use in various settings, including clinics and outreach programs. Their ease of use and speed enable healthcare providers to identify and initiate treatment for hepatitis C patients promptly, reducing the risk of transmission and improving patient outcomes.
On the other hand, ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) tests, although typically requiring more time to process, offer high sensitivity and specificity. ELISA tests can detect antibodies against the hepatitis viruses in the blood, ensuring accurate diagnosis. By combining the immediacy of rapid tests with the reliability of ELISA tests, healthcare systems can effectively manage and control the spread of hepatitis C, facilitating early intervention and better health management for affected individuals.
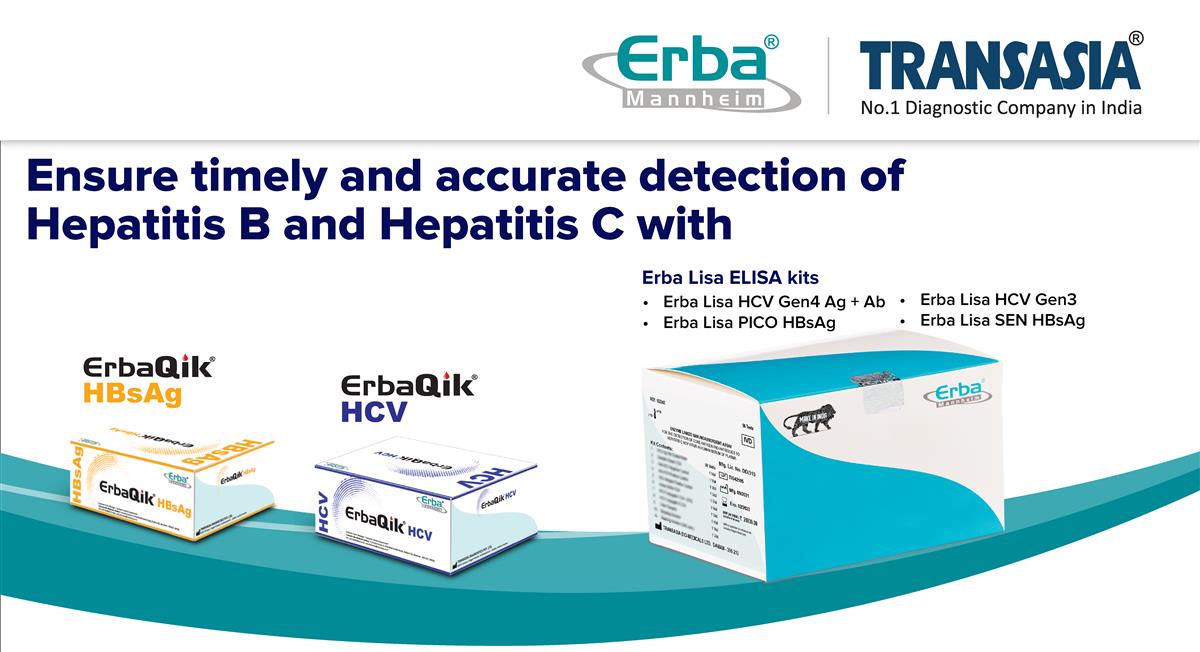
Erba Transasia’s role in timely detection of Hepatitis B and C
Erba Transasia’s extensive diagnostic solutions for timely detection of Hepatitis B and C comprise of rapid and ELISA screening kits, including Erba Lisa HCV Gen 4 Ag + Ab, Erba Lisa HCV Gen 3 V2, Erba Lisa PICO HBsAg, Erba Lisa SEN HBsAg, ErbaQik HBsAg test card and Erba Qik HCV test card.
The ErbaLisa HCV Gen4 Ag+Ab is India’s first and only indigenously developed 4th generation immunoassay for HCV detection, which is an ELISA for the qualitative detection of HCV-cAg and anti-HCV antibodies in human serum and plasma, together in same well. It uses monoclonal antibodies to HCV-cAg and a mixture of Core, NS3, NS4 and NS5 recombinant proteins of Hepatitis C virus, and is adaptable on fully automated analyzers (FAAs). ErbaLisa SEN HBsAg is a fourth generation ultra sensitive enzyme linked immunoassay assay for detection of HBsAg uses the sandwich ELISA technique allowing qualitative detection of as low as 0.1ng/mL of HBsAg in patient serum / plasma. The kit is designed for use in blood banks to screen infected units and for clinical diagnostic laboratories. ErbaQik HBsAg test is one step in-vitro Immunochromatographic assay designed for qualitative determination of Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in Human serum or plasma.
Timely detection of hepatitis B and C is essential for effective disease management and prevention. Rapid tests and ELISA play complementary roles in the diagnostic process, each offering unique benefits that enhance the overall effectiveness of hepatitis screening programs. By leveraging these diagnostic tools, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes, reduce transmission rates, and contribute to the global effort to combat hepatitis B and C.
Reference:
-
Hepatitis | World Health Organization. Available at: https://www.who.int/india/health-topics/hepatitis ; accessed on 12 July, 2024.