The Role of ANA Testing in Autoimmune Disorders Diagnosis and Management
Autoimmune Disorders are amongst the most important non-communicable diseases. There are more than 80 autoimmune diseases affecting approximately 100 million people worldwide. In India, the field of rheumatology is emerging therefore data on the different autoimmune disorders is sparse.
A person with an autoimmune disorder definitely has a malfunctioning immune system, which has failed to differentiate between the non-self and self-proteins and is producing autoantibodies directed against its own proteins.
Autoimmune disorders can be classified as organ specific – characterized by response against autoantigens localized to a particular organ, and non-organ specific – directed against autoantigens present throughout the body.
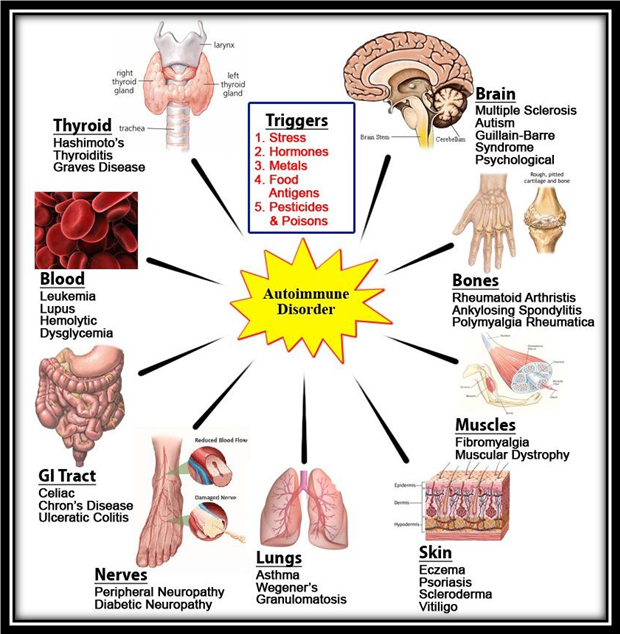
The clinical detection of autoimmune disorders is an important measure because effective treatment starts only after its diagnosis and in most cases, early treatment may help in minimizing the severity to much extent.
ANA Testing
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as Antinuclear Factor or ANFs) are autoantibodies that are reactive with the antigens in the nucleoplasm.
ANA test is used to determine the presence of autoantibodies against self-antigens representing cellular components such as chromatin, histone, nucleic acid, nuclear and ribonuclear protein. These autoantibodies probably occur in the circulation of all human beings, but an ANA test is considered positive only if they occur at titers elevated significantly above the normal serum level.
ANA Antinuclear antibodies test is an excellent diagnostic test for disorders associated with autoimmunity, which includes conditions such as – active/inactive Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, scleroderma, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis, multiple sclerosis, discoid lupus, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, anti-phospholipid syndrome, psoriatic arthritis, and certain cancers.
Autoantibodies against the following cellular antigens are detected in ANA testing:
- dsDNA. dsDNA autoantibodies target the cellular dsDNA. These are found to be present in the patients suffering from SLE and are considered to be the hallmark of SLE, if present in significant levels
- Nucleosomes. Nucleosome autoantibodies recognize histone complex, and are indicative of SLE
- Histones. Anti-histone antibodies against histone-DNA complex, in the absence of other autoantibodies, are characteristic marker of drug-induced SLE
- Sm. Smith (Sm) antigens are small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Anti-Sm antibodies are highly specific and serve as useful markers in diagnosis and classification of SLE
- PCNA. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen is highly specific for SLE. It is a useful tool to detect activated lymphocytes
- SSA/Ro. Ro (SSA) complex is one of the ANA which have specific reactivity and are known to be present in lupus and Sjogren’s syndrome
- U1-SnRNP. U1-SnRNP autoantibody is prevalent in mixed connective tissue disorder
- SSB/La. SSB autoantibodies are found in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome, neonatal lupus and progressive systemic sclerosis. It is also a marker for B-lymphocyte activation
- CENP-B. Anti-centromere antibody against CENP-B is considered as a diagnostic marker of CREST syndrome, a type of systemic sclerosis
- SCL-70. Anti-SCL 70 antibodies are directed against DNA topoisomerase I. They are specifically found in progressive systemic sclerosis patients
- AMA-M2. Anti-mitochondrial M2 antibody are useful for the detection of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)
- Jo-1. Patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis can be diagnosed by detection of anti-Jo-1 antibodies
- Mi-2. Anti-Mi-2 antibodies serve as a hallmark of dermatomyositis
- Ku. Anti-Ku antibodies are associated with connective tissue diseases and inflammatory myopathies.
Although, core reason of autoimmunity is not evident, its management helps to eliminate the development and painful symptoms to much extent. Early diagnosis and treatment ensures the minimum severity and can eliminate the worse outcomes.
There are two types of ELISA methods currently used for ANA testing. One is the generic assay which detects ANA of broad specificity, while the other is antigen specific assay that detects ANA and reacts with a single autoantigen i.e. dsDNA, SS-A/Ro, SS-B/La, Scl-70, Sm, Sm/RNP etc.
In antigen specific assay multiple antigens are coated on to microtitre plates, usually a combination of SSA/Ro, SSB/La, Sm, and U1-RNP, with many also including Jo-1 and Scl70. This test is both highly specific and sensitive and substantially decreases the time involved when screening large numbers of patient samples. The test is simple to perform, can be automated and does not require highly trained operators who can recognize microscopic patterns. The ELISA is therefore, one of most widely used method not only for routine screening, but also for detection of specific ANA.
Transasia Bio-Medicals Ltd. offers US-FDA approved Diamedix Is® ANA Screen ELISA, an apt solution for diagnosis of autoimmune disorders.
References
- Anti-nuclear Antibody – Wikipedia
- Kumar Y., Bhatia A. & Minz R.W. (2009). Antinuclear antibodies and their detection methods in diagnosis of connective tissue diseases: a journey revisited. Diagnostic Pathology, 4.
- Prem Kumar B, Srinivasa Murthy M , Rajagopal K , Nagaprabu VN and Sree Madhuri P. Epidemiology of Autoimmune Disorders with Special Reference to Rheumatoid Arthritis from a Tertiary Care Center. Indian Journal of Pharmacy Practice, Vol 7, Issue 3, Jul–Sep, 2014.